Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 processing of clustered DNA damage
processing of clustered DNA damage鹿園 直哉; 赤松 憲; 高橋 桃子*; 野口 実穂; 漆原 あゆみ; O'Neill, P.*; 横谷 明徳
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 749(1-2), p.9 - 15, 2013/09
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:36.83(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)クラスターDNA損傷は、電離放射線によってDNAへリックス二回転中に二つ以上の損傷が生じるものである。クラスターDNA損傷がどの程度、また、どのように生物影響を及ぼすのかに関しては不明な点が多い。本研究では、鎖切断と脱塩基部位や8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG)を含むクラスターDNA損傷を用い、大腸菌に形質転換し、形質転換効率及び突然変異頻度を調べた。鎖切断と脱塩基部位からなるクラスターDNA損傷の場合、鎖切断及び脱塩基部位がそれぞれ単独であった場合に対し、形質転換効率は大幅に低下することが明らかになった。損傷間の距離を離す(10-20bp)と、形質転換効率はDNA polymerase I(Pol I)の作用により回復した。一方、鎖切断と8-oxoGからなるクラスターDNA損傷の場合、クラスターDNA損傷による突然変異頻度はPol Iの働きによって低下することが明らかとなった。これらの結果は、クラスターDNA損傷による生物効果にPol Iが深く関与することを示している。
 -rays in
-rays in 
豊島 快幸*; 高橋 明珠*; 田中 寿基*; 渡部 潤*; 茂木 喜信*; 山崎 達雄*; 濱田 涼子*; 岩下 和裕*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 740(1-2), p.43 - 49, 2012/12
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:49.23(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology) is a fungus that is used widely in traditional Japanese fermentation industries. In this study, the lethal and mutagenic effects of different linear energy transfer (LET) radiation in freeze-dried conidia of
is a fungus that is used widely in traditional Japanese fermentation industries. In this study, the lethal and mutagenic effects of different linear energy transfer (LET) radiation in freeze-dried conidia of  were investigated. The lethal effect, which was evaluated by a 90% lethal dose, was dependent on the LET value of the ionizing radiation. The most lethal ionizing radiation among that tested was
were investigated. The lethal effect, which was evaluated by a 90% lethal dose, was dependent on the LET value of the ionizing radiation. The most lethal ionizing radiation among that tested was  C
C ion beams with an LET of 121 keV/
ion beams with an LET of 121 keV/ m. The
m. The  C
C ion beams had a 3.6-times higher lethal effect than low-LET (0.2 keV/
ion beams had a 3.6-times higher lethal effect than low-LET (0.2 keV/ m)
m)  -rays. The mutagenic effect was evaluated by the frequency of selenate resistant mutants.
-rays. The mutagenic effect was evaluated by the frequency of selenate resistant mutants.  C
C ion beams with an LET of 86 keV/
ion beams with an LET of 86 keV/ m were the most effective in inducing selenate resistance. The mutant frequency following exposure to
m were the most effective in inducing selenate resistance. The mutant frequency following exposure to  C
C ion beams increased with an increase in dose and reached 3.47
ion beams increased with an increase in dose and reached 3.47  10
10 at 700 Gy. In the dose range from 0 to 700 Gy,
at 700 Gy. In the dose range from 0 to 700 Gy,  C
C ion beams were the second most effective in inducing selenate resistance, the mutant frequency of which reached a maximum peak (1.67
ion beams were the second most effective in inducing selenate resistance, the mutant frequency of which reached a maximum peak (1.67  10
10 ) at 400 Gy. To elucidate the characteristics of mutation induced by ionizing radiation, mutations in the sulphate permease gene (
) at 400 Gy. To elucidate the characteristics of mutation induced by ionizing radiation, mutations in the sulphate permease gene (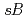 ) and ATP sulfurylase gene (
) and ATP sulfurylase gene (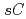 ) loci, the loss of function of which results in a selenate resistant phenotype, were compared between
) loci, the loss of function of which results in a selenate resistant phenotype, were compared between  C
C ion beams and
ion beams and  -rays. We detected all types of transversions and transitions. For frameshifts, the frequency of a +1 frameshift was the highest in all cases. Although the incidence of deletions
-rays. We detected all types of transversions and transitions. For frameshifts, the frequency of a +1 frameshift was the highest in all cases. Although the incidence of deletions  2 bp was generally low, deletions
2 bp was generally low, deletions  20 bp were characteristic for
20 bp were characteristic for  C
C ion beams.
ion beams.  -rays had a tendency to generate mutants carrying a multitude of mutations in the same locus. Both forms of radiation also induced genome-wide large-scale mutations including chromosome rearrangements and large deletions.
-rays had a tendency to generate mutants carrying a multitude of mutations in the same locus. Both forms of radiation also induced genome-wide large-scale mutations including chromosome rearrangements and large deletions.
野口 実穂; 漆原 あゆみ; 横谷 明徳; O'Neill, P.*; 鹿園 直哉
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 732(1-2), p.34 - 42, 2012/04
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:45.3(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)In vivoにおいて塩基損傷を伴った鎖切断の効果はいまだ多くが不明である。本研究においてわれわれは1ヌクレオチドgap(GAP)と8-oxoGから成るクラスターDNA損傷の突然変異誘発性について明らかにした。MutY欠損株において、GAPと8-oxoGの2つの損傷から成り、これらが相補鎖にまたがって存在するクラスター損傷の変異頻度は8-oxoGとAPサイトから成るクラスター損傷とほぼ同じ値を示したことから、クラスター損傷内において、GAPはAPサイトと同様に処理されることが示唆された。GAPと8-oxoGが同一鎖上に存在するクラスター損傷の変異頻度は8-oxoG単独損傷とほぼ等しい値であった。3つの損傷から成るクラスター損傷(GAPと8-oxoGが相補鎖、その同一鎖上にもう一つの8-oxoG)の変異頻度は8-oxoG単独損傷より高い値であったが、2つの8-oxoGが相補鎖にまたがって存在するクラスター損傷に比べて低い値であった。これらの結果から、クラスター損傷内にGAPが存在する場合、存在しない場合に比べて、8-oxoGの鋳型として向いに挿入されるヌクレオチドの変異誘発性が低くなることが示唆された。さらに、GAPの修復は相補鎖の8-oxoGにより阻害されるが、同一鎖の8-oxoGには阻害されないことが示唆され、GAPの修復が生物影響に大きく影響を与えることが示された。
長谷 純宏; 吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 鳴海 一成
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 731(1-2), p.41 - 47, 2012/03
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:72.04(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)植物におけるイオンビームの変異誘発効果に関する知見を深めるため、飛程末端に近い炭素イオン(平均LET 425keV/ m)と種子を透過する炭素イオン(平均LET 113keV/
m)と種子を透過する炭素イオン(平均LET 113keV/ m)の変異効果を比較した。照射した植物体からの大腸菌由来
m)の変異効果を比較した。照射した植物体からの大腸菌由来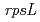 遺伝子のプラスミドレスキュー法では、113keV/
遺伝子のプラスミドレスキュー法では、113keV/ m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が2.7倍上昇したのに対して、425keV/
m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が2.7倍上昇したのに対して、425keV/ m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が上昇しなかったことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンで誘発される突然変異は、プラスミドレスキューでは検出できないことが示唆された。非相同末端結合修復能を欠損するシロイヌナズナのDNA ligase IV遺伝子の変異体は、両者の炭素イオンに対して野生型よりも高い感受性を示したが、野生型と変異体の感受性の差は425keV/
m炭素イオンでは変異頻度が上昇しなかったことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンで誘発される突然変異は、プラスミドレスキューでは検出できないことが示唆された。非相同末端結合修復能を欠損するシロイヌナズナのDNA ligase IV遺伝子の変異体は、両者の炭素イオンに対して野生型よりも高い感受性を示したが、野生型と変異体の感受性の差は425keV/ m炭素イオンでは113keV/
m炭素イオンでは113keV/ m炭素イオンに比べて極めて小さいことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンは修復困難なDNA損傷を誘発することが示唆された。シロイヌナズナの
m炭素イオンに比べて極めて小さいことから、飛程末端に近い炭素イオンは修復困難なDNA損傷を誘発することが示唆された。シロイヌナズナの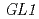 遺伝子を利用した変異解析では、無毛変異の形成頻度は両者の炭素イオンで差がなかったが、大規模な欠失変異(
遺伝子を利用した変異解析では、無毛変異の形成頻度は両者の炭素イオンで差がなかったが、大規模な欠失変異(
 30kb)の頻度は425keV/
30kb)の頻度は425keV/ m炭素イオンが6倍高かったことから、LETが高まるに従って大規模な欠失変異の割合が高まることが示唆された。
m炭素イオンが6倍高かったことから、LETが高まるに従って大規模な欠失変異の割合が高まることが示唆された。
 -ray-irradiated tobacco cells; Evidence for radiation-induced genomic instability in plant cells
-ray-irradiated tobacco cells; Evidence for radiation-induced genomic instability in plant cells横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 長谷 純宏; 浜田 信行*; 小林 泰彦; 田中 淳; 鳴海 一成
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 691(1-2), p.41 - 46, 2010/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:28.46(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)電離放射線を照射した哺乳類細胞や酵母では、その子孫細胞において、直接照射されていないにもかかわらず、染色体異常や突然変異の頻度が高い現象(放射線誘発ゲノム不安定性)が報告されてきた。本研究の目的は、高等植物に放射線誘発ゲノム不安定性が生じるか否かを明らかにすることである。そこで、 線を照射したタバコ細胞とその子孫細胞において、微小核頻度と増殖を調べた。照射細胞の細胞周期は、照射の24時間前後で一過性に停止した。一方、微小核頻度は照射後48時間で最大となった。照射細胞の約半数は微小核を有したが、照射細胞は非照射細胞と同程度に旺盛な増殖を示した。照射細胞は照射後4週間で2の21乗倍に増殖したが、微小核頻度は非照射細胞と比べてなお2倍高かった。この実験結果は、照射子孫細胞において微小核が誘発され続けていることを示しており、タバコ細胞における放射線誘発ゲノム不安定性の直接の証拠となる。
線を照射したタバコ細胞とその子孫細胞において、微小核頻度と増殖を調べた。照射細胞の細胞周期は、照射の24時間前後で一過性に停止した。一方、微小核頻度は照射後48時間で最大となった。照射細胞の約半数は微小核を有したが、照射細胞は非照射細胞と同程度に旺盛な増殖を示した。照射細胞は照射後4週間で2の21乗倍に増殖したが、微小核頻度は非照射細胞と比べてなお2倍高かった。この実験結果は、照射子孫細胞において微小核が誘発され続けていることを示しており、タバコ細胞における放射線誘発ゲノム不安定性の直接の証拠となる。
鹿園 直哉; O'Neill, P.*
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 669(1-2), p.162 - 168, 2009/11
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:44.68(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)To gain insights into the processing of bistranded base lesions, several potential repair intermediates following 8-oxoG removal from bistranded clusters containing 8-oxoG and DHT were assessed. Clusters, such as DHT/AP and DHT/GAP have relatively low mutation frequencies, whereas clusters, such as AP/AP or GAP/AP, significantly reduce the number of transformed colonies, most probably through formation of a lethal DSB. These results suggest that bistranded base lesions, but not clusters containing only AP sites and strand breaks, are repaired in a coordinated manner so that the formation of DSBs is avoided. We propose that, when either base lesion is initially excised from a bistranded base damage site, the remaining base lesion will only rarely be converted into an AP site or a single strand break in vivo.
岩川 眞由美*; 浜田 信行*; 今留 香織*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦; 今井 高志*
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 642(1-2), p.57 - 67, 2008/07
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:66.2(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)We performed microarray analysis of irradiated and bystander fibroblasts in confluent cultures. To see the effects in bystander cells, each of 1, 5 and 25 sites was targeted with 10 particles of carbon ions using microbeams, where particles traversed 0.00026, 0.0013 and 0.0066% of cells, respectively. To see the effects in irradiated cells, cultures were exposed to 10% survival dose (D), 0.1D and 0.01D of corresponding broadbeams. Irrespective of the target numbers (1, 5 or 25 sites) and the time (2 or 6 h postirradiation), similar expression changes were observed in bystander cells. Among 874 probes that showed more than 1.5-fold changes in bystander cells, 25% were upregulated and the remainder downregulated. These included genes related to cell communication, stress response and cell cycle. Pathway analysis revealed serial bystander activation of G protein/PI-3 kinase pathways. Instead, genes related to cell cycle or death and cell communication were upregulated in irradiated cells, but not in bystander cells. Our results indicate different expression profiles in irradiated and bystander cells, and imply that intercellular signaling between irradiated and bystander cells activate intracellular signaling, leading to the transcriptional stress response in bystander cells.
浜田 信行*; Ni, M.*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 639(1-2), p.35 - 44, 2008/03
被引用回数:47 パーセンタイル:77.48(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)ヒト正常線維芽細胞における重粒子線照射後誘導蛋白質を定量的ウェスタンブロット法によって解析した。 Cイオン(220MeV)又は
Cイオン(220MeV)又は Neイオン(260MeV)をD
Neイオン(260MeV)をD 相当線量、すなわちCでは1.3Gy(7.6
相当線量、すなわちCでは1.3Gy(7.6 10
10 p/cm
p/cm )、Neでは1.9Gy(2.7
)、Neでは1.9Gy(2.7 10
10 p/cm
p/cm )をブロードビームで照射した細胞では、p53蛋白質Ser15部位でのリン酸化レベルが、照射後2時間と6時間とで変化せず高いレベルを保持していた。一方、高密度培養した細胞シャーレ内の1
)をブロードビームで照射した細胞では、p53蛋白質Ser15部位でのリン酸化レベルが、照射後2時間と6時間とで変化せず高いレベルを保持していた。一方、高密度培養した細胞シャーレ内の1 25か所に1か所あたり10粒子照射した場合の、細胞シャーレ内の圧倒的多数をしめるバイスタンダー細胞では、照射後2時間よりも6時間で上昇することがわかった。この結果は、直接の重イオン照射細胞と非照射のバイスタンダー細胞における分子応答機構の違いを示唆している。
25か所に1か所あたり10粒子照射した場合の、細胞シャーレ内の圧倒的多数をしめるバイスタンダー細胞では、照射後2時間よりも6時間で上昇することがわかった。この結果は、直接の重イオン照射細胞と非照射のバイスタンダー細胞における分子応答機構の違いを示唆している。
浜田 信行*; 原 孝光*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 637(1-2), p.190 - 196, 2008/01
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:49.95(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)重粒子線を照射したヒト正常線維芽細胞の生存子孫細胞において、最初に与えられた線量とそのLET値(線エネルギー付与)に依存してコロニー形成能が遅延的に低下することを、これまでにわれわれは明らかにしてきた。今回、照射によって線量・線質依存的に引き起こされた分化の進行の結果、分裂能が低下した細胞が生存子孫細胞の中に誘発されることが、このような放射線誘発遺伝的不安定性の機序である可能性を示した。

松尾 裕一郎*; 西嶋 茂宏*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 田中 淳; 清水 喜久雄*
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 602(1-2), p.7 - 13, 2006/12
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:58.31(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)真核生物におけるイオンビーム誘発突然変異の特徴を解析する目的で、出芽酵母 に対する炭素イオン照射の効果を
に対する炭素イオン照射の効果を 線照射の効果と比較した。酵母
線照射の効果と比較した。酵母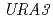 遺伝子をマーカーとして、炭素イオンビームによって誘発された54個の
遺伝子をマーカーとして、炭素イオンビームによって誘発された54個の 突然変異をシークエンスし、突然変異の特異性を解析した。その結果、炭素イオンビームによって誘発された突然変異の種類は、トランスバージョンが68.7%, トランジションが13.7%で、挿入/欠失は17.6%であった。トランスバージョンはおもに、G:C塩基対からT:A塩基対へ置換であったのに対し、トランジションのすべてはG:C塩基対からA:T塩基対への置換であった。突然変異が生じた塩基の周辺の配列を比較すると、ACA又はACT配列の真ん中のCが置換されているケースが多く見られた。高等植物であるシロイヌナズナに対しては、イオンビームは短い欠失や染色体の再編成を生じさせることが報告されているが、これとは対照的に酵母では大きな欠失や配列の重複はみられなかった。さらに、酵母におけるイオンビーム誘発突然変異で最も特徴的だったのは、ヌクレオソーム構造のリンカー領域の付近に変異が集中し、ホットスポットを形成している点である。一方、
突然変異をシークエンスし、突然変異の特異性を解析した。その結果、炭素イオンビームによって誘発された突然変異の種類は、トランスバージョンが68.7%, トランジションが13.7%で、挿入/欠失は17.6%であった。トランスバージョンはおもに、G:C塩基対からT:A塩基対へ置換であったのに対し、トランジションのすべてはG:C塩基対からA:T塩基対への置換であった。突然変異が生じた塩基の周辺の配列を比較すると、ACA又はACT配列の真ん中のCが置換されているケースが多く見られた。高等植物であるシロイヌナズナに対しては、イオンビームは短い欠失や染色体の再編成を生じさせることが報告されているが、これとは対照的に酵母では大きな欠失や配列の重複はみられなかった。さらに、酵母におけるイオンビーム誘発突然変異で最も特徴的だったのは、ヌクレオソーム構造のリンカー領域の付近に変異が集中し、ホットスポットを形成している点である。一方、 線ではこのようなホットスポットは見られなかった。このことから、炭素イオンビームは、DNA配列とヌクレオソーム構造の両方に依存して突然変異を誘発させていることが示唆された。
線ではこのようなホットスポットは見られなかった。このことから、炭素イオンビームは、DNA配列とヌクレオソーム構造の両方に依存して突然変異を誘発させていることが示唆された。
 PprA protein
PprA protein佐藤 勝也*; 和田 成一; 菊地 正博; 舟山 知夫; 鳴海 一成; 小林 泰彦
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 596(1-2), p.36 - 42, 2006/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:10.91(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)われわれは、過去の研究で、デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスの放射線耐性に重要な役割を果たしている新規タンパク質PprAを同定した。この研究では、哺乳動物細胞のDNA損傷応答を評価するために、鎖切断を持つ2本鎖DNAを認識して結合するというPprAタンパク質の性質に着目し、放射線で生じるDNA鎖切断を免疫蛍光法で可視化する技術の開発を試みた。放射線照射直後におけるCHO-K1細胞核へのPprAタンパク質の結合の増加は、このタンパク質がDNA鎖切断部位に結合していることを示唆している。また、細胞の脆弱化条件を変えることで、放射線照射直後のCHO-K1細胞のミトコンドリアDNAへのPprAタンパク質の結合を検出することも可能であった。今回開発した方法は、培養細胞のDNA損傷応答の評価に有用であるとともに、環境や薬学分野における遺伝毒性試験にも応用可能であると考えられる。